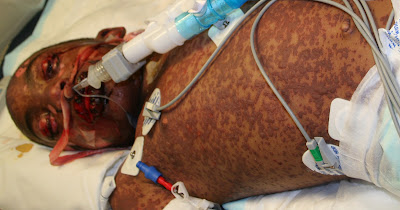
Stevens Johnson syndrome is an uncommon but serious and life-threatening skin condition characterized by ulcerated grazes on the mucous membranes and skin. Stevens Johnson syndrome is also called as Erythema multiforme major. In this diffuse and severe disorder, mucous membranes and skin react severely to infection or a medication. This syndrome initiates with flu-like symptoms and followed by a sore purplish or red rash that blisters and spreads which ultimately cause the death and shedding of skin’s top layer.
Causes
It is very difficult to identify the exact cause of Stevens Johnson syndrome. However, the condition is considered as an allergic reaction in response to infection, medication or illness.
Diagnosis
The complications which can develop due to SJS include:
Hospitalization is essential in most patients presenting with SJS. Treatment focuses on controlling symptoms, eliminating the underlying cause and minimizing complications. In severe cases, intensive supportive care such as specialized care in a burn unit is vital.
Stop medication
Image source: dermatlas.med.jhmi.edu
Any age group can be affected with Stevens Johnson syndrome. However, older people are at higher risk of the disorder because they tend to use more drugs associated with the disorder, so it occurs more commonly in older people. AIDS patient are also at a higher risk of this disorder.Causes
It is very difficult to identify the exact cause of Stevens Johnson syndrome. However, the condition is considered as an allergic reaction in response to infection, medication or illness.
- Medication causes: This disorder is often caused by the conventional drugs. Drugs usually associated with it are NSAIDs like Paracetamol, Anti-gout medications like allopurinol, Anticonvulsants, Barbiturates, Penicillins and sulfa antibiotics.
- Infectious causes: In some cases, it is caused by an infection such as HIV, Herpes, Diphtheria, Typhoid, Influenza and Hepatitis.
- Genetic: Carrying a HLA-B12 gene may increase the risk for SJS.
- Rare causes: It may be caused by physical stimuli, given through ultraviolet light or radiation therapy.
- Other causes: Existing therapeutic conditions which lessen the body immunity. For instance, SLE (systemic lupus erythematosus) or HIV (human immunodeficiency virus) may make you susceptible to this disorder.
- Stevens Johnson syndrome begins with non-specific symptoms such as Fever, Cough, Sore throat, Burning eyes, Aching, Headaches, Vomiting and Diarrhoea. Usually, these symptoms are misdiagnosed and treated with antibiotics.
- A purple or red skin rash which spread within hours to days
- Mysterious widespread skin pain
- Tongue swelling
- Facial swelling
- Hives
- Blisters on mucous membranes and skin, especially in mouth, eyes, nose and genital areas
- Shedding of skin
Diagnosis
- SJS can be identified on the basis of medical history, clinical findings, a physical exam and distinctive signs and symptoms of disorder.
- It can be confirmed with a skin biopsy or a direct immune fluorescence study.
The complications which can develop due to SJS include:
- Eye problems: When the rash caused by SJS involves the eye, it can lead to irritation & dry eyes in mild cases. In severe cases, it may cause scarring and extensive tissue damage within your eyes that can lead to blindness.
- Internal organs damage: SJS may cause lesions in internal organs that can lead to inflammation of the liver, kidney, lungs and heart.
- Secondary skin infection: Acute skin infection of SJS can cause life-threatening complications such as meningitis.
- Permanent skin damage: When skin recovers from SJS; abnormal bumps, scars and coloring may remain on skin. Toenails and fingernails may not grow normally.
- Sepsis: When infective bacteria pass through bloodstream and spread throughout body, life-threatening condition Sepsis occurs. Sepsis is a quickly progressing condition that can lead to shock and organ failure.
Treatment
Hospitalization is essential in most patients presenting with SJS. Treatment focuses on controlling symptoms, eliminating the underlying cause and minimizing complications. In severe cases, intensive supportive care such as specialized care in a burn unit is vital.
Stop medication
- If the cause of SJS is drug related, immediately discontinue the medications. It is difficult to determine the SJS causing drug, so it is essential to stop taking all nonessential medications.
- Suitable antibiotics to control infection
- Pain killers to reduce discomfort
- Topical steroids to decrease skin inflammation
- Antihistamines to ease itching
- Intravenous immunoglobulin can be given in severe cases to halt the further process
- Oral and topical corticosteroids to treat the affected areas
- Intravenous corticosteroids to reduce the severity of symptoms and cut down recovery time in adults
- Fluid replacement: Fluid replacement is a significant part of treatment because loss of skin may cause loss of fluids from the body. Fluids and nutrients are provided via a tube placed through nose which is delivered into stomach.
- Eye care: It is essential to consult an ophthalmologist because there is a risk of eye damage with SJS.
- Wound care: While blisters heal, cool and wet compresses helps to ease them.
- Skin grafting is a process of removing skin from one part of the body and attaching it on another part or attaching a synthetic skin substitute. This treatment is rarely required, when the large area of body is affected.








0 comments:
Post a Comment